
Years ago, scientists noticed a series of curving bands of layered rock within Jezero Crater that they dubbed “the curvilinear unit.” They could see these layers from space but are finally able to see them up close, thanks to Perseverance. “It’s been a delight to look at rocks on another planet and see processes that are so familiar,” Ives said. With a background in studying Earth-based rivers, Ives has spent the last six months analyzing images of the Red Planet’s surface. The more powerful the flow of water, the more easily it’s able to move larger pieces of material,” said Libby Ives, a postdoctoral researcher at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California, which operates the Perseverance rover. “Those indicate a high-energy river that’s truckin’ and carrying a lot of debris. Stitched together from hundreds of images captured by Perseverance’s Mastcam-Z instrument, two new mosaics suggest the latter, revealing important clues: coarse sediment grains and cobbles.
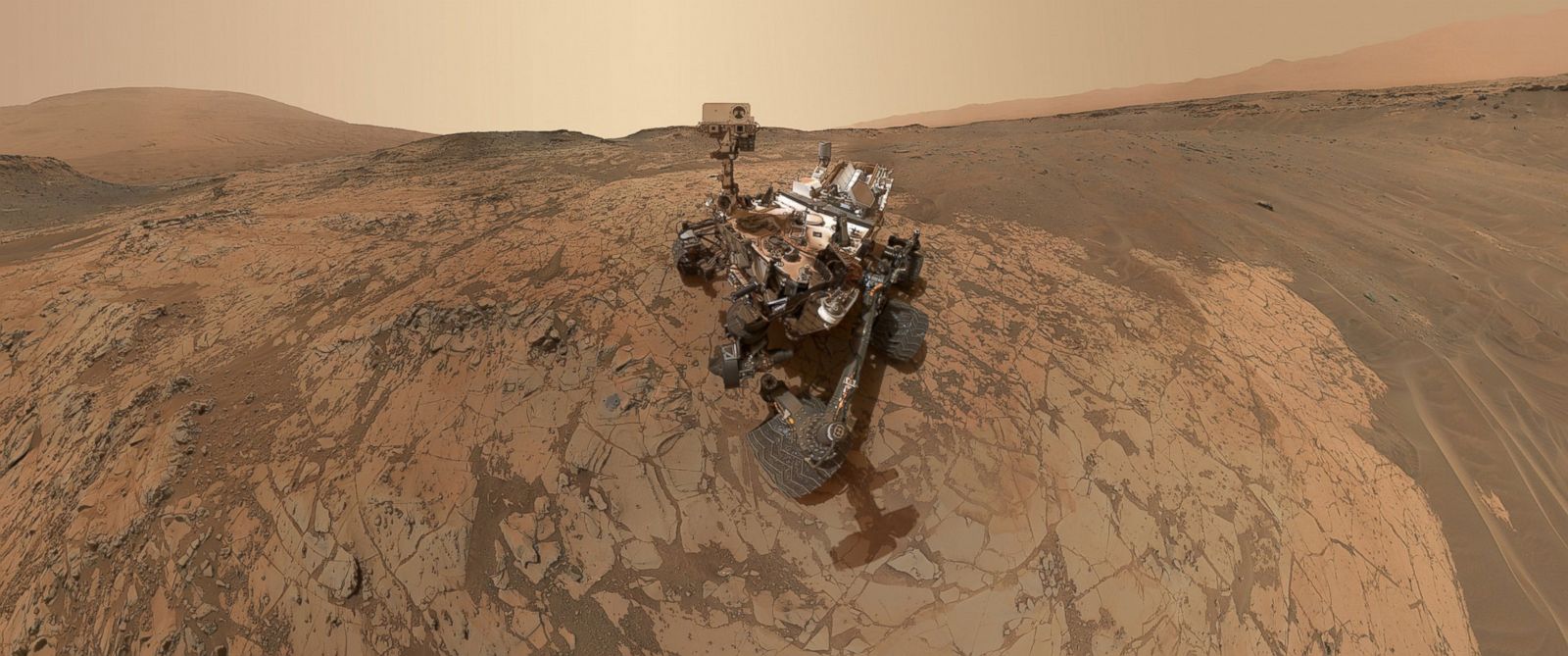

One question scientists want to answer is whether that water flowed in relatively shallow streams – closer to what NASA’s Curiosity rover has found evidence of in Gale Crater – or a more powerful river system. Perseverance is exploring the top of a fan-shaped pile of sedimentary rock that stands 820 feet (250 meters) tall and features curving layers suggestive of flowing water. Understanding these watery environments could help scientists in their efforts to seek out signs of ancient microbial life that may have been preserved in Martian rock. The river was part of a network of waterways that flowed into Jezero Crater, the area the rover has been exploring since landing more than two years ago. New images taken by NASA’s Perseverance rover may show signs of what was once a rollicking river on Mars, one that was deeper and faster-moving than scientists have ever seen evidence for in the past. Evidence left in rocks is leading scientists to rethink what watery environments looked like on ancient Mars.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
